316L NPT3/4 Conductivity 20μS/cm EC Sensor Resistivity Sensor
>>Technical Parameter
Conductivity Range: 0.01~20μS/cm
Resistivity Range: 0.01~18.2MΩ·cm
Electrode Mode: 2-pole
Electrode Constant: K≈0.01
Wetted Material: 316L
Temperature Range: 0~60℃
Pressure Rating: 0~0.6MPa
Temperature Sensor: NTC10K/NTC2.2K/PT100/PT1000
Installation Interface: NPT3/4
Electrode Cable: Standard 10m
>>Principle
Since water contains various dissolved salts that exist in the form
of ions, when electrodes are inserted into the water and an
electric current is applied, the charged ions move in specific
directions under the influence of the electric field. The anions in
water migrate toward the anode, enabling the aqueous solution to
conduct electricity. The ability of water to conduct electricity is
termed conductivity.
Conductivity is the reciprocal of resistivity and reflects the
total dissolved salt content in water, serving as a critical
indicator for assessing water quality. It reveals the concentration
of electrolytes present in water. Depending on the concentration of
electrolytes in an aqueous solution, the degree of electrical
conduction varies. By measuring the conductivity of a solution, the
solubility of electrolytes can be analyzed. This forms the
fundamental analytical principle of conductivity meters.
Conductivity exhibits significant temperature dependence. For
metals, conductivity decreases with rising temperatures, whereas
for semiconductors, it increases with temperature. In solid
semiconductors, doping levels can drastically alter
conductivity—higher doping concentrations result in greater
conductivity.
The conductivity of aqueous solutions depends on the concentration
of dissolved salts or other chemical impurities that dissociate
into electrolytes. The conductivity of a water sample serves as a
key metric for measuring its salt content, ionic components, and
impurity levels. Lower conductivity (higher resistivity) indicates
purer water.
Water conductivity is often recorded as specific conductance, which represents the conductivity of water at a standardized
temperature of 25°C.
>>Installation Diagram
Before use, unscrew the electrode protective cap and install it
with the appropriate mounting bracket or accessories.
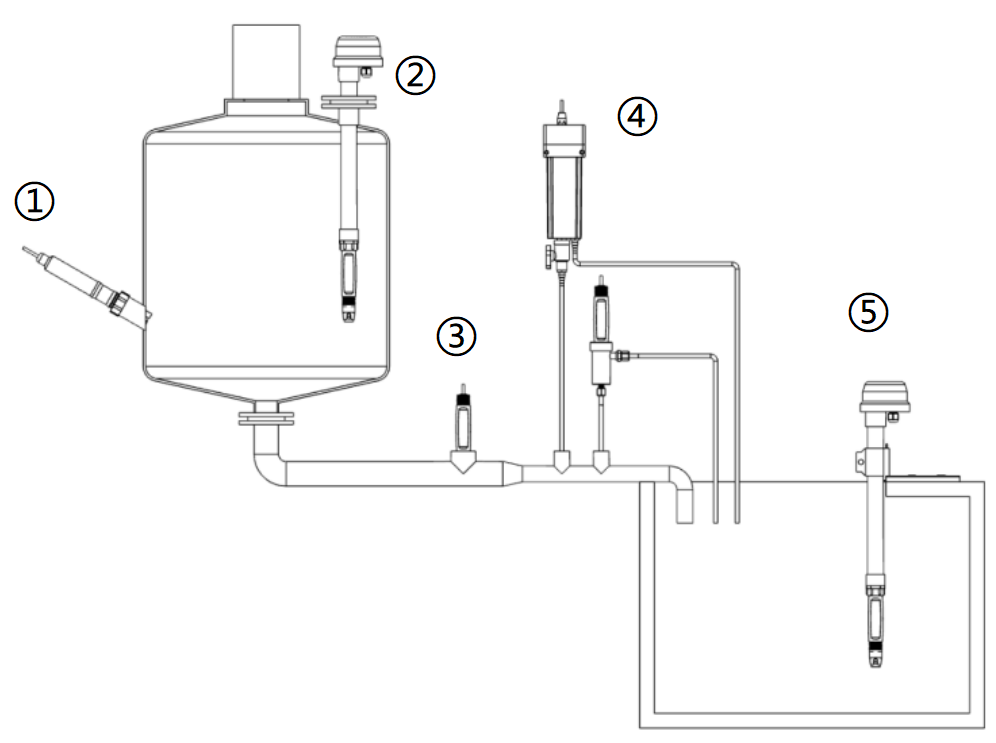
1. Sidewall Installation: Ensure the interface tilt angle exceeds 15 degrees.
2. Top Flange Installation: Note flange dimensions and electrode insertion depth.
3. Pipe Installation: Consider pipe diameter, flow velocity, and pressure.
4. Flow-Through Installation: Monitor flow velocity and pressure.
5. Submersion Installation: Adjust bracket length as needed.








